Imagine accessing powerful software without the headache of installation, maintenance, or hefty upfront costs. Sound appealing? That’s the promise of Software as a Service, or SaaS. This revolutionary model is transforming how businesses and individuals alike interact with technology.
Instead of owning software outright, you subscribe to it, accessing it over the internet like a streaming service for your applications. Why is this important? Well, SaaS is driving unprecedented agility and innovation, allowing companies to scale quickly and focus on their core competencies rather than IT infrastructure.
In this article, we’ll delve into the core principles of SaaS, explore its myriad benefits, and address some common challenges, empowering you to understand and leverage this game-changing technology to its fullest potential.
Understanding Software as a Service (SaaS)
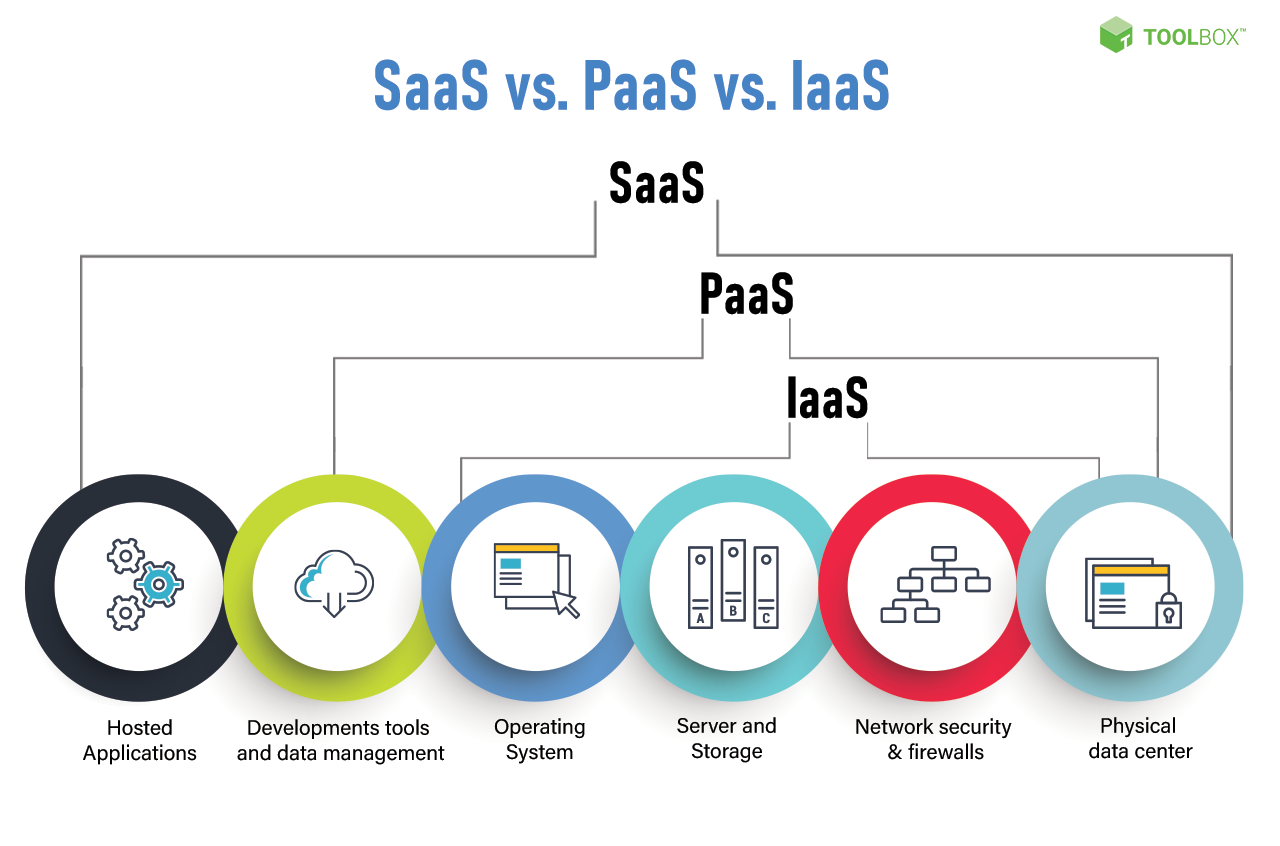
SaaS has transformed how organizations obtain and employ software. It moves away from conventional installations to a model that offers accessibility and adaptability.
Think of it as renting an application instead of owning it outright. You’re paying for access and utilization, not the program itself.
This hosted solution is typically accessed over the internet. It handles everything from maintenance to updates, delivering a hands-off experience.
Businesses leverage SaaS to cut costs, boost productivity, and focus on their core activities. It levels the playing field, providing resources to businesses of all sizes.
The beauty of SaaS lies in its versatility. From customer relationship management to project management, diverse applications find a home in the SaaS ecosystem.
The Core Benefits of Using SaaS
Cost reduction is a major appeal. Avoid hefty upfront expenses for licensing and hardware. Instead, predictable subscription fees make budgeting manageable.
SaaS facilitates scalability. Resources can be adjusted up or down based on current needs. This flexibility translates into efficiency and minimizes waste.
Automatic updates are standard with SaaS solutions. Say goodbye to manual patching and installations. Always stay current with the newest features.
Accessibility from any device offers huge advantages. As long as you have a web browser and an internet connection, you can tap into crucial data and programs.
Collaboration becomes easier with SaaS. Multiple people can access and contribute from different locations. This improves teamwork and efficiency.
SaaS products generally integrate well with other systems. Connecting with existing infrastructure enables easier workflow and reduces data silos.
Exploring Different Types of SaaS Solutions
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) streamlines interactions with clients. Platforms such as Salesforce assist with managing data and communications.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business functions. Oracle NetSuite and SAP Business ByDesign centralize data and processes.
Collaboration and Communication tools enhance teamwork. Solutions like Slack and Microsoft Teams foster real-time interaction and information sharing.
Project Management platforms enable teams to plan and execute projects effectively. Products such as Asana and Trello help with task tracking and milestones.
Human Resource Management (HRM) systems streamline HR processes. Tools such as BambooHR and Workday manage employee data and payroll tasks.
Marketing Automation enhances the efficiency of marketing. Hubspot and Marketo are examples of systems that automate tasks such as email campaigns.
SaaS Deployment Models and Considerations
Multi-tenancy architecture allows several users to share the same infrastructure. This results in cost-effectiveness and efficient resource utilization.
Single-tenancy provides a dedicated instance of the software for each customer. Offering higher levels of customization, this also results in increased privacy.
Hybrid models involve integrating SaaS solutions with on-premises systems. This approach allows a gradual transition to the cloud, balancing needs and resources.
When choosing a SaaS solution, you must consider data security. Ensure the provider implements powerful security measures to safeguard sensitive data.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) describe the guarantees of uptime and support. Knowing the provider’s obligations will lead to a better understanding of your rights.
Integration capabilities affect how well the SaaS solution communicates. Select a platform that interfaces smoothly with your present systems.
The Future of SaaS: Trends and Predictions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) drive innovation in SaaS. These technologies enable features such as predictive analytics and process automation.
Low-code/No-code platforms democratize software development. Making it simpler for non-technical staff to construct custom applications.
Microservices architecture drives flexibility and scalability in SaaS. Breaking down large applications into smaller, manageable components.
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source. This enables reduced latency and enhanced efficiency for applications.
Vertical SaaS solutions are designed for particular industry needs. Offering specialized capabilities and value compared to general solutions.
SaaS is continually evolving to match modern requirements. Expect more creativity, greater personalization, and closer integration with emerging technologies.